Introduction
The viral infection this attacks the liver before causing the dangerous complications cirrhosis and liver cancer together with potential fatal consequences for those not treated.
The world experiences this virus transmission at significant public health levels even though vaccines exist for protection against it.
Global estimates indicate that 296 million people maintain active this virus infection in their bodies. The infection spreads most widely among three priority groups who work in healthcare or participate in drug injection or maintain several sexual relationships.
We will analyze Hepatitis B transmission routes within communities together with public health outcomes and the most beneficial methods to cease transmission and minimize its population spread.
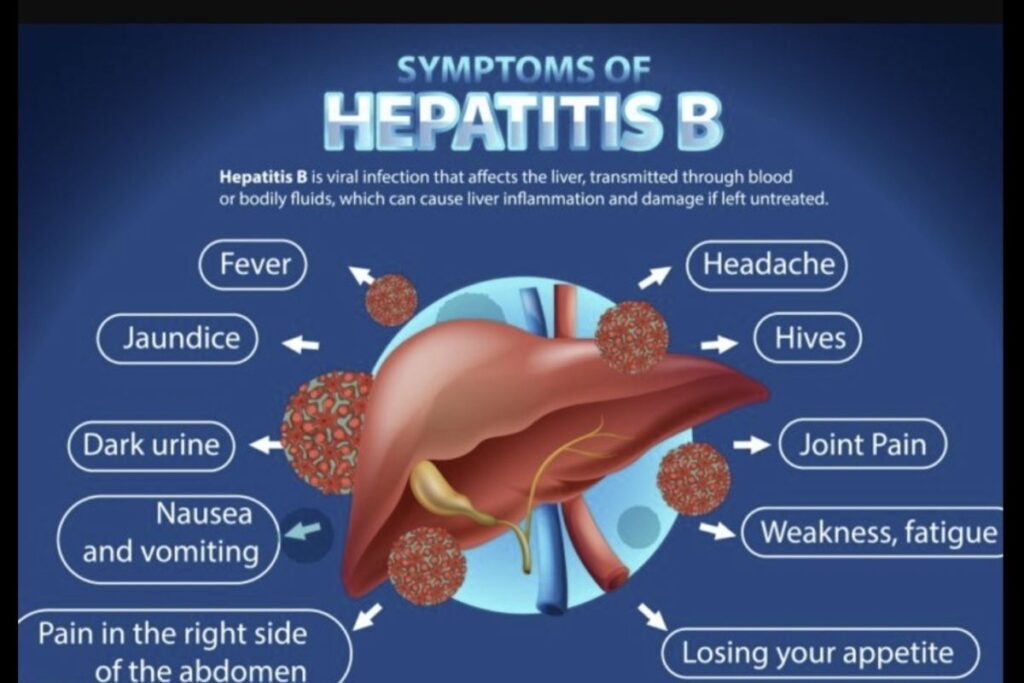
What is Hepatitis B?
- The Hepatitis B virus known as HBV leads to liver infections with inflammation and eventual tissue scarring in the course of long-term disease progression.
- Certain aspects of HBV infection behavior lead to the development of chronic conditions leading to major liver diseases including cirrhosis along with hepatocellular carcinoma (liver cancer).
- The virus finds its way through activities including unprotected sex and needs spread by blood as well as semen and other human fluids.
- Unprotected sex with an infected individual Drug users who share their needles with others or their drug equipment about during these activities will transmit this virus to the person they interact with.
- Mother-to-child transmission during childbirth Medical workers encounter this transmission route through needle-stick injuries in addition to healthcare-related blood contamination.
- A person who uses personal items with an infected individual runs high risk of infection. Because this withstands outside human bodily exposure without decay it spreads rapidly through communities without proper healthcare or vaccination options.
How Hepatitis B Spreads
Among Populations Protecting others from Hepatitis B requires complete knowledge about the different ways the virus transmits from person to person. Every person becomes vulnerable to the virus after exposure through unprotected contact with the virus.
🔘 Mother-to-Child Transmission
Hepatitis B transmission occurs most frequently between mothers and their babies during birth within high-prevalence regions.
The passage of Hepatitis B virus from a mother to her baby occurs during the delivery process. Since children who catch hepatitis B at an early age tend to develop into chronic this patients their risk of severe liver damage increases.
A low vaccination rate against this creates public health problems because mother-to-child transmission continues to occur frequently between parents and newborns.
🔘 Sexual Transmission
Experiencing unprotected sexual relations with a person carrying the hepatitis B virus represents a significant means by which the infection spreads between individuals.
Unprotected intercourse between people who have this results in transmission because the virus exists in semen and vaginal fluids.
Individuals who practice risky sexual activities encounters increased risk of this infection because they have multiple sex partners or do commercial sex work.
🔘 Transmission Through Injection Drug Use
People who inject drugs acquire this from sharing needles and drug application accessories during their drug use activities.
People who share bleach-free needles and syringes put themselves at risk for exposed blood during use since viruses live in blood thus triggering thisB infection.
Injection drug users suffer discrimination from their communities and several nations lack sufficient needle exchange programs that help prevent this from spreading among these vulnerable populations.

🔘 Healthcare-Associated Transmission
Healthcare workers and their patients who receive treatment in healthcare establishments face possible Hepatitis B transmission risks.
The virus enters bloodstream creating an infection through contact between needles and bloodstream as well as exposure to infected medical equipment.
The absence of proper healthcare hygiene practices together with inadequate sterilization of medical equipment creates high-risk situations for this transmission.
The Global Impact of Hepatitis B
- The infection rates of this create substantial public health problems because it affects hundreds of millions of people throughout the world. The following information demonstrates the severe scale of this problem in numbers:
- Chronic this infection affects 296 million people throughout the worldwide region. Approximately 820,000 fatalities occur annually because of Chronic Hepatitis B through liver cancer together with cirrhosis.
- Hepatitis B infection generates its highest burden within sub-Saharan Africa together with East Asia and the Pacific Islands because the virus remains endemic there.
- The adult population of these affected areas faces Hepatitis B chronic infection at a rate reaching up to 10%. The considerable costs related to this treatment and hospitalization and liver transplantation strain medical services especially in poor and developing nations.
- Embedding this infection results in health effects which remain persistent throughout the life span. People who live with ongoing this infection face various forms of discrimination and social rejection together with restricted access to work opportunities and educational resources and beneficial services which worsens their financial situation.
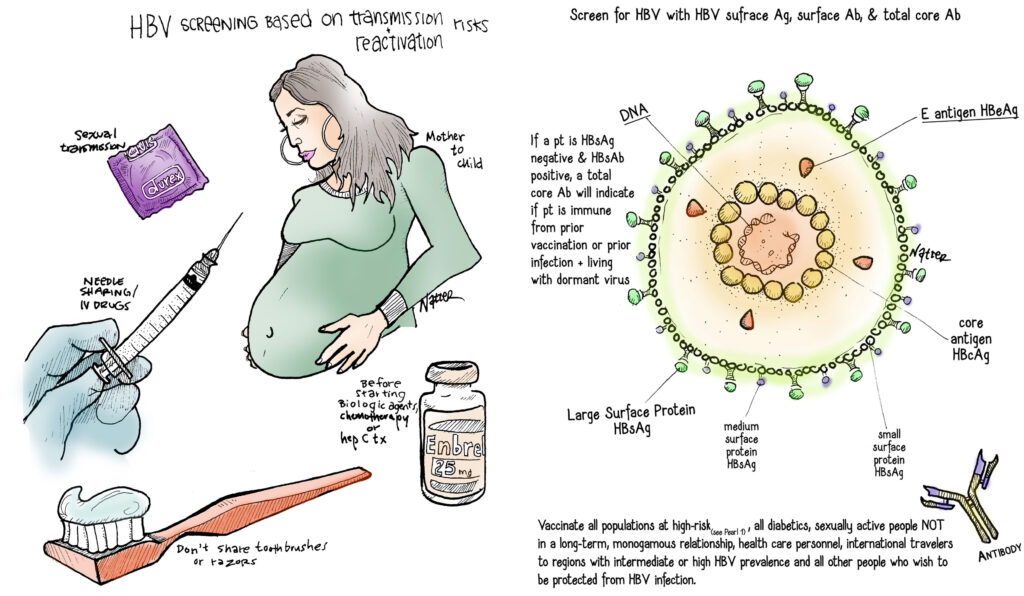
Ways to Stop Hepatitis B Transmission
The prevention of Hepatitis B transmission exists through multiple effective approaches that help decrease disease burden in the population. The following represents the best methods for preventing Hepatitis B transmission:
| 🔘 Vaccination The Hepatitis B Vaccine stands as the most effective means to stop the transmission of Hepatitis B. Vaccination proves effective in blocking Hepatitis B infections and medical authorities utilize it worldwide to cut transmission levels. Many nations use universal vaccination plans through newborn infant vaccination soon after the birth process. Health authorities incorporate this vaccine for standard use in child vaccination programs. Vaccinating young children along with infants decreases their chances of contracting Hepatitis B infection. Vaccination campaigns for older children along with adults who belong to high-risk groups enable reduction of Hepatitis B spread when disease prevalence is high. Vaccines become crucial for persons whose behaviors raise infection risks including drug injectors and individuals who practice risky sexual activities. |
| 🔘 Harm Reduction Programs exist as a vital service for individuals who inject drugs. The prevention of Hepatitis B transmission for individuals who use injection drugs depends heavily on harm reduction programs being prioritized. These programs include: Needle Exchange Programs set up clean needle distribution to stop the transmission of infections during drug injections among those who use needles to administer drugs. Safe Injection Facilities create supervised drug use areas which provide sterile equipment for drug administrations to decrease needle and syringe exchange among users. |
| 🔘 Improved Healthcare Infection Control All healthcare institutions must establish thorough infection control protocols which stop Hepatitis B from spreading between patients and medical personnel. These measures include: The protection of healthcare workers against Hepatitis B bloodborne pathogens happens through universal precautions that require them to use gloves together with gowns and masks. Medical tools require sterilization or must be used only once to stop the virus from spreading. The implementation of Hepatitis B Vaccination for healthcare personnel remains essential to block the medical facility transfer of Hepatitis B virus because it safeguards medical workers from infection. |
| 🔘 Safe Sexual Practices The reduction of sexual transmission requires proper education which teaches individuals to practice safe sexual activities. Sexual protection through condom usage must accompany the practice of having less than multiple sexual relationships. Health authorities should motivate high-risk group members to obtain vaccination against Hepatitis B. |
| 🔘 Screening and Early Detection The detection of Hepatitis B infection remains important to perform regular testing on people identified at high risk including pregnant women who use drugs for injections along with individuals maintaining multiple sexual relationships. The diagnosis during early phases provides suitable treatment methods alongside monitoring that minimizes the potential development of complications including liver damage and cancer. |
Conclusion
The global health problem of hepatitis B keeps causing significant issues particularly among populations at high risk The prevention of Hepatitis B.
Transmission becomes possible through extensive understanding of its spreading methods and the implementation of vaccination programs as well as proper sexual practices and improved healthcare systems alongside harm reduction programs.