Eczema, also known as atopic dermatitis, is a chronic skin condition that affects millions of people worldwide. It is characterized by inflamed, itchy, and dry skin that can be both uncomfortable and unsightly. While the exact cause of eczema is still not fully understood, there are several factors that contribute to the onset and flare-ups of the condition. Understanding the triggers, managing symptoms effectively, and exploring the various treatment options available can help individuals living with eczema maintain better skin health.

In this article, we will explore what eczema is, how to identify common triggers, how to manage its symptoms, and the latest treatment options for better skin care.
Table of Contents
- Introduction: What is Eczema?
- Understanding the Causes of Eczema
- Common Triggers of Eczema
- Symptoms of Eczema
- Managing Eczema Symptoms
- Treatment Options for Eczema
- 6.1 Topical Treatments
- 6.2 Oral Medications
- 6.3 Light Therapy
- 6.4 Natural Remedies
- Prevention Tips for Eczema Flare-ups
- Conclusion: Living with Eczema
Introduction: What is Eczema?
Eczema is a term used to describe a group of skin conditions that cause inflammation, redness, and irritation. The most common form of eczema is atopic dermatitis, which is a chronic, long-lasting condition that often starts in childhood. Eczema can occur anywhere on the body but is commonly found on the face, hands, feet, and behind the knees.
While eczema is not contagious, it can significantly affect a person’s quality of life due to itching, discomfort, and visible flare-ups. The exact cause of eczema remains unclear, but it is believed to be a combination of genetic and environmental factors. People with eczema often have an overactive immune response, which leads to inflammation when the skin is exposed to certain triggers.
Understanding the Causes of Eczema
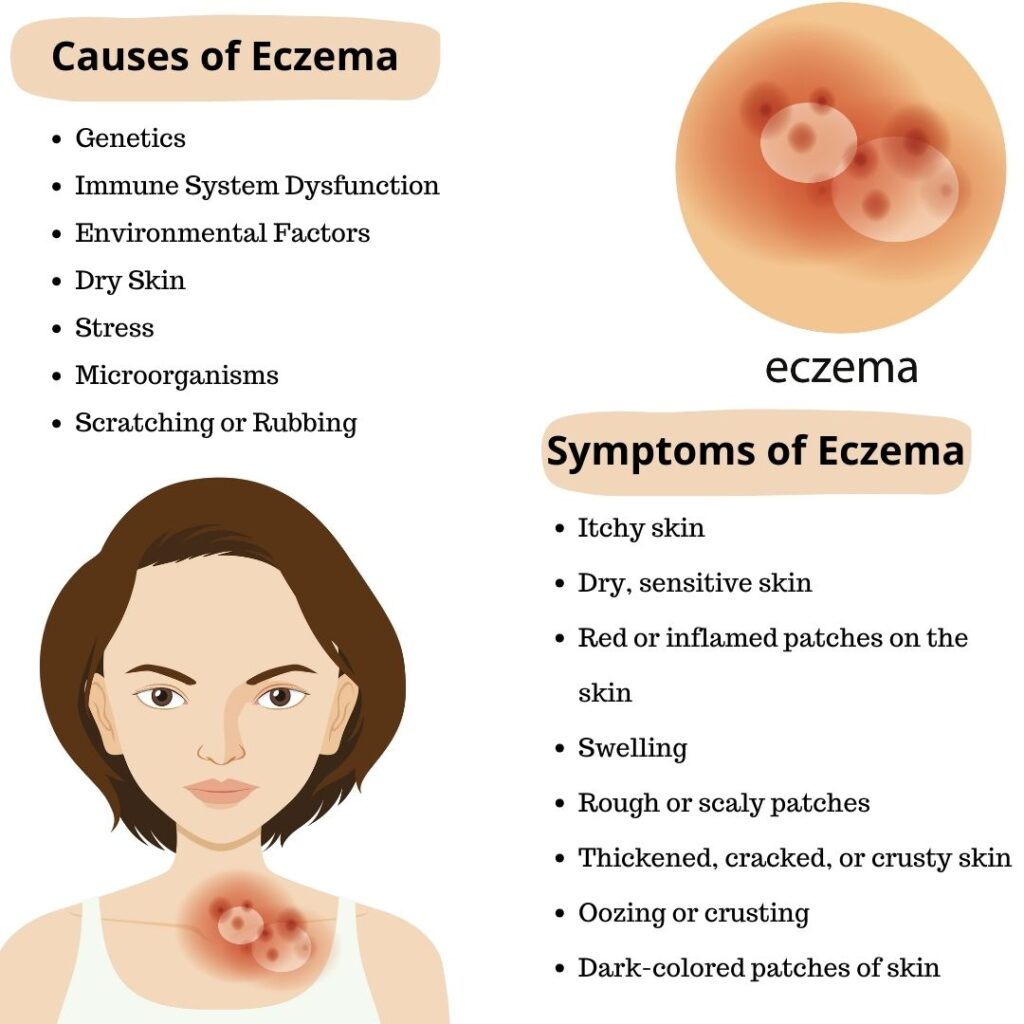
The causes of eczema are complex and still under research. However, it is widely understood that a combination of genetic and environmental factors contributes to the development of eczema. People with a family history of eczema, asthma, or hay fever are more likely to develop the condition.
1. Genetic Factors
Genetics play a crucial role in the development of eczema. Certain genes are associated with the skin’s ability to form a protective barrier. People with eczema often have a mutation in the gene responsible for producing filaggrin, a protein that helps form the skin’s outermost layer. This dysfunction can result in a compromised skin barrier, making it easier for irritants, allergens, and microbes to penetrate the skin and cause inflammation.
2. Immune System Response
Eczema is also linked to an overactive immune system. When the immune system overreacts to harmless substances, it leads to the inflammation and itching characteristic of eczema.
Common Triggers of Eczema
While eczema can be managed, certain environmental, lifestyle, and dietary factors can trigger flare-ups. Understanding these triggers can help reduce the frequency and severity of symptoms.
3.1 Environmental Factors
Environmental factors are one of the most common causes of eczema flare-ups. These include:
- Weather: Extreme weather conditions, particularly cold or dry air, can lead to skin dryness, making eczema worse.
- Allergens: Pollen, mold, pet dander, and dust mites can cause allergic reactions that aggravate eczema.
- Pollution: Air pollutants and chemicals can irritate sensitive skin, triggering flare-ups.
3.2 Dietary Triggers
Certain foods may exacerbate eczema symptoms, though these triggers vary from person to person. Common food allergens include:
- Dairy products
- Eggs
- Nuts
- Wheat
- Soy
- Seafood
It’s important to monitor your diet and identify any food items that may be causing your eczema to worsen.
3.3 Stress and Emotional Triggers
Emotional stress and anxiety are well-known triggers for eczema flare-ups. When stressed, the body produces hormones that can increase inflammation in the skin, leading to more severe eczema symptoms. Managing stress through relaxation techniques like yoga or meditation can help prevent flare-ups.
3.4 Skin Care Products
Certain ingredients in skin care products, such as fragrances, dyes, and harsh chemicals, can irritate the skin and trigger eczema. It’s essential to use products specifically formulated for sensitive skin and free from these irritating components.
Symptoms of Eczema
Eczema symptoms can vary depending on the severity of the condition. Common symptoms include:
- Itchy, dry skin
- Red, inflamed patches of skin
- Thickened skin from constant scratching
- Blisters and oozing sores in severe cases
- Cracked, scaly skin
The severity of eczema symptoms can range from mild dryness to severe inflammation and pain. Identifying symptoms early on can help prevent further complications, such as skin infections and scarring.
Managing Eczema Symptoms
While eczema cannot be cured, there are several methods to manage and relieve symptoms.
5.1 Moisturization
Moisturizing is the cornerstone of eczema management. Using thick, emollient-based moisturizers can help restore the skin’s natural barrier and prevent dryness. Apply moisturizers immediately after bathing while the skin is still damp to lock in moisture.
5.2 Topical Steroids and Medications
Topical corticosteroids are commonly prescribed to reduce inflammation and relieve itching. These are available in different strengths, depending on the severity of eczema. In more severe cases, oral medications or immunosuppressive drugs may be recommended to manage inflammation.
5.3 Lifestyle Modifications
Certain lifestyle changes can significantly improve eczema symptoms:
- Avoiding long, hot showers that can dry out the skin.
- Wearing soft, breathable fabrics like cotton to avoid skin irritation.
- Keeping nails short to reduce the risk of scratching and further skin damage.
5.4 Avoiding Scratching and Irritation
Scratching can worsen eczema symptoms and lead to skin infections. It’s essential to avoid scratching even though it may be difficult due to the intense itching. Consider wearing cotton gloves at night or using anti-itch creams to alleviate discomfort.
Treatment Options for Eczema
There are various treatment options available to help manage eczema, ranging from topical treatments to advanced therapies.
6.1 Topical Treatments
Topical treatments such as corticosteroid creams, calcineurin inhibitors (like tacrolimus), and emollient-based moisturizers are essential for managing eczema. These treatments help reduce inflammation, prevent dryness, and control flare-ups.
6.2 Oral Medications
Oral medications, such as antihistamines to relieve itching or oral corticosteroids for severe flare-ups, may be prescribed by a healthcare provider. In cases of moderate to severe eczema, oral immunosuppressive medications like methotrexate or cyclosporine may be used.
6.3 Light Therapy
For chronic eczema, phototherapy or light therapy may be used. This treatment involves exposing the skin to ultraviolet (UV) light under medical supervision to reduce inflammation and improve the skin’s appearance.
6.4 Natural Remedies
Some people with eczema find relief from natural remedies such as aloe vera, coconut oil, and chamomile tea compresses. However, it’s essential to consult a healthcare professional before using these remedies, as they may not be suitable for everyone.
Prevention Tips for Eczema Flare-ups
While eczema cannot be fully cured, certain preventive measures can help reduce flare-ups and improve skin health.
7.1 Maintain a Consistent Skin Care Routine
Adopting a daily skincare routine that includes moisturizing and gentle cleansing can help keep eczema under control.
7.2 Choose the Right Fabrics
Wear soft, breathable fabrics such as cotton to minimize irritation. Avoid wool and synthetic materials that can exacerbate eczema symptoms.
7.3 Avoid Hot Water and Harsh Soaps
Use lukewarm water instead of hot water and opt for gentle, fragrance-free soaps. Harsh soaps and hot water can strip the skin of its natural oils, leading to dryness and irritation.
Conclusion: Living with Eczema
Eczema is a challenging but manageable condition. By understanding the triggers, symptoms, and treatment options available, individuals can take steps to improve their skin health and quality of life. Identifying triggers, maintaining a proper skincare routine, and using appropriate treatments can help minimize flare-ups and promote healthier skin.
If you struggle with eczema, it’s important to consult a dermatologist to tailor a treatment plan that works best for your skin. With the right approach, managing eczema becomes easier, and clear, healthy skin is within reach.