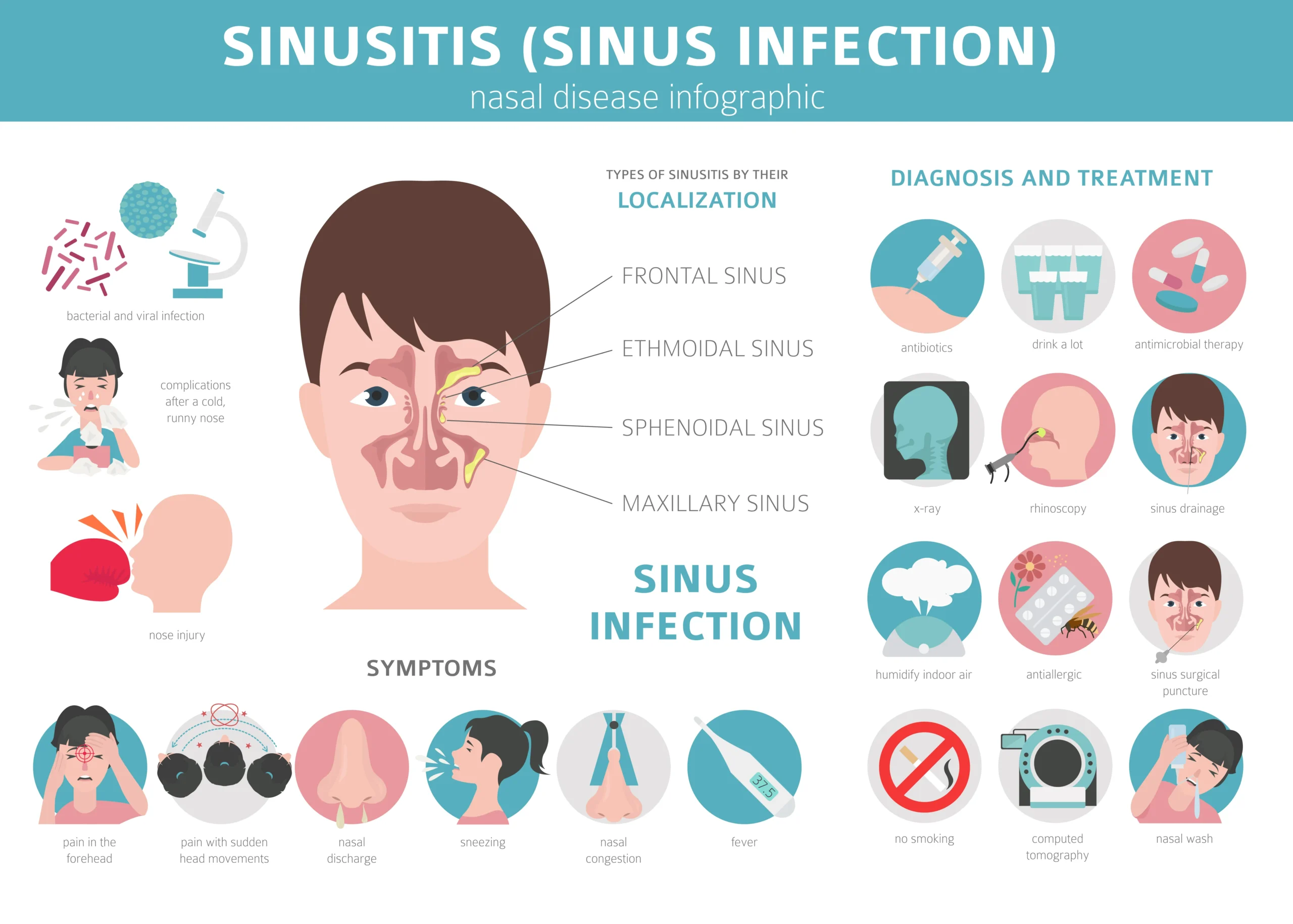
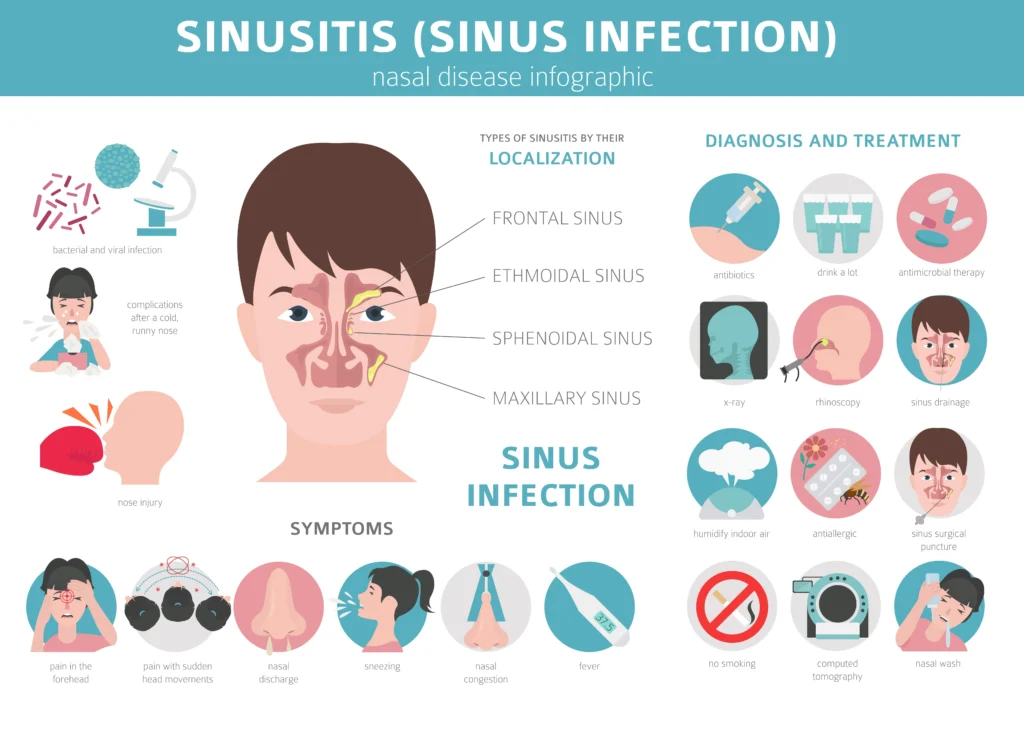
Introduction to Chronic Sinusitis
Chronic sinusitis is a long-term inflammation of the sinuses that lasts for more than 12 weeks despite treatment. It affects millions worldwide, causing persistent nasal congestion, facial pain, and difficulty breathing. Understanding its causes, symptoms, and treatments can help in managing and preventing complications.
Understanding Sinusitis: Acute vs. Chronic
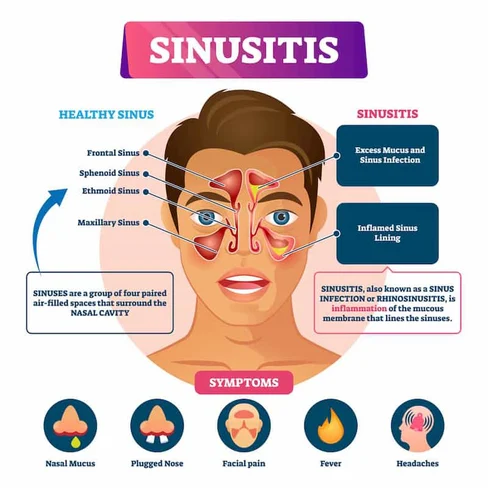
Sinusitis occurs when the sinuses, air-filled spaces in the skull, become inflamed due to infection, allergies, or other factors. There are two main types:
- Acute Sinusitis – Short-term inflammation lasting less than four weeks, often caused by viral infections like the common cold.
- Chronic Sinusitis – Persistent inflammation lasting more than 12 weeks, usually due to underlying conditions such as allergies, nasal polyps, or bacterial infections.
Causes of Chronic Sinusitis
Several factors contribute to chronic sinusitis, including:
- Infections – Bacterial, viral, or fungal infections can cause long-term inflammation.
- Nasal Polyps – Growths in the nasal passages that block airflow and drainage.
- Allergies – Allergic reactions to dust, pollen, or mold can lead to sinus inflammation.
- Deviated Nasal Septum – A crooked septum can obstruct sinus drainage, leading to chronic infections.
- Weak Immune System – Conditions like HIV, diabetes, or chemotherapy treatments can make the body more susceptible to sinus infections.
- Environmental Factors – Exposure to smoke, pollutants, or dry air can contribute to chronic sinusitis.
Symptoms of Chronic Sinusitis
Common symptoms include:
- Persistent nasal congestion
- Thick, discolored nasal discharge
- Facial pain or pressure, especially around the eyes, nose, and forehead
- Headaches and ear pain
- Postnasal drip (mucus dripping down the throat)
- Cough, often worse at night
- Reduced or lost sense of smell and taste
- Fatigue and irritability
Diagnosis and Medical Tests
A doctor will diagnose chronic sinusitis based on symptoms and medical tests, including:
- Physical Examination – Checking for nasal inflammation and blockages.
- Nasal Endoscopy – Using a thin, flexible tube with a camera to examine the sinuses.
- Imaging Tests – CT scans or MRI scans provide detailed images of the sinuses to detect blockages or infections.
- Allergy Testing – Identifies allergic triggers that contribute to sinusitis.
- Mucus Culture – A lab test to identify bacterial or fungal infections.
Treatment Options for Chronic Sinusitis
Effective treatments help reduce inflammation and improve sinus drainage. Options include:
1. Medications
- Nasal Corticosteroids – Reduce inflammation and swelling (e.g., Fluticasone, Budesonide).
- Saline Nasal Irrigation – Rinsing the nasal passages with saline solution to clear mucus.
- Antibiotics – If a bacterial infection is present, a doctor may prescribe antibiotics.
- Antihistamines – Help control allergies that contribute to chronic sinusitis.
- Decongestants – Reduce nasal swelling and improve airflow.
2. Surgical Options
For severe cases, surgery may be necessary:
- Functional Endoscopic Sinus Surgery (FESS) – A minimally invasive procedure to remove blockages and improve drainage.
- Balloon Sinuplasty – A less invasive method that uses a small balloon to widen sinus passages.
- Polypectomy – Removing nasal polyps to improve airflow.
Home Remedies and Lifestyle Changes
In addition to medical treatment, home remedies can help manage symptoms:
- Steam Inhalation – Breathing in steam from a bowl of hot water can loosen mucus.
- Hydration – Drinking plenty of fluids helps thin mucus for better drainage.
- Humidifiers – Adding moisture to the air prevents nasal dryness.
- Rest and Proper Nutrition – Strengthening the immune system with a healthy diet and adequate rest.
- Avoiding Triggers – Reducing exposure to allergens, smoke, and pollutants.
Prevention Tips
To prevent chronic sinusitis from recurring:
- Maintain good nasal hygiene with saline rinses.
- Manage allergies with medications or allergen avoidance.
- Quit smoking and reduce exposure to pollutants.
- Practice good hand hygiene to prevent infections.
- Seek early treatment for sinus infections before they become chronic.
Conclusion
Chronic sinusitis is a persistent condition that can significantly affect daily life. However, with the right treatments, lifestyle changes, and preventive measures, symptoms can be managed effectively. If you experience long-term sinus problems, consult a healthcare professional for proper diagnosis and treatment. Taking proactive steps can help you breathe easier and improve your quality of life.