Introduction to Anxiety Disorders
Anxiety disorders are among the most common mental health conditions, affecting millions worldwide. While occasional anxiety is a normal response to stress, persistent and excessive worry can interfere with daily life. This article explores the types, causes, symptoms, and effective coping mechanisms for anxiety disorders.
Types of Anxiety Disorders
Anxiety disorders encompass several conditions, each with distinct characteristics. Understanding these types helps in identifying symptoms and seeking appropriate treatment.

Generalized Anxiety Disorder (GAD)
GAD involves chronic and excessive worry about various aspects of life, such as work, health, and relationships. Symptoms include restlessness, fatigue, difficulty concentrating, and sleep disturbances.
Panic Disorder
Panic disorder is characterized by sudden, intense episodes of fear, often accompanied by physical symptoms such as heart palpitations, dizziness, and shortness of breath. Panic attacks can occur unexpectedly and cause significant distress.
Social Anxiety Disorder
Social anxiety disorder (social phobia) involves an overwhelming fear of social situations. Individuals may experience extreme self-consciousness, fear of judgment, and avoidance of social interactions.
Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder (OCD)
OCD is marked by intrusive thoughts (obsessions) and repetitive behaviors (compulsions) aimed at reducing anxiety. Common compulsions include excessive handwashing, checking, and arranging objects.
Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD)
PTSD develops after exposure to traumatic events such as accidents, abuse, or war. Symptoms include flashbacks, nightmares, heightened anxiety, and emotional numbness.
Specific Phobias
Specific phobias involve an intense, irrational fear of particular objects or situations, such as heights, spiders, or flying. Avoidance behavior is common in individuals with phobias.
Causes of Anxiety Disorders
Several factors contribute to the development of anxiety disorders, including:
- Genetics – A family history of anxiety increases the likelihood of developing the condition.
- Brain Chemistry – Imbalances in neurotransmitters like serotonin and dopamine can lead to heightened anxiety.
- Environmental Factors – Stressful life events, trauma, or childhood experiences can trigger anxiety disorders.
- Personality Traits – Individuals with perfectionist or highly self-critical tendencies may be more prone to anxiety.
- Substance Use – Excessive alcohol, caffeine, or drug use can contribute to anxiety symptoms.
Symptoms of Anxiety Disorders
Symptoms vary depending on the type of anxiety disorder but commonly include:
- Persistent and excessive worry
- Restlessness or nervousness
- Increased heart rate or palpitations
- Sweating and trembling
- Difficulty concentrating
- Sleep disturbances
- Avoidance of anxiety-inducing situations
Diagnosis and Tests
Anxiety disorders are diagnosed through:
- Clinical Interviews – Mental health professionals assess symptoms, medical history, and personal experiences.
- Psychological Assessments – Standardized questionnaires and scales help measure anxiety levels.
- Medical Tests – Blood tests and imaging may be used to rule out physical conditions causing anxiety symptoms.
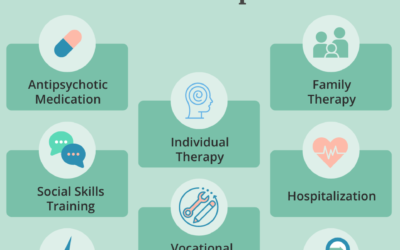
Treatment Options
Effective treatment for anxiety disorders includes:
1. Medications
- Selective Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitors (SSRIs) – Commonly prescribed antidepressants (e.g., Fluoxetine, Sertraline) that help regulate mood.
- Benzodiazepines – Fast-acting medications (e.g., Alprazolam, Lorazepam) used for short-term relief.
- Beta-Blockers – Help control physical symptoms such as rapid heartbeat and trembling.
2. Psychotherapy
- Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) – Helps individuals identify and modify negative thought patterns contributing to anxiety.
- Exposure Therapy – Gradual exposure to feared situations reduces avoidance behavior and anxiety response.
- Mindfulness-Based Therapy – Teaches relaxation techniques to manage anxious thoughts and emotions.
3. Alternative Therapies
- Yoga and Meditation – Promotes relaxation and reduces stress.
- Herbal Remedies – Some natural supplements, such as chamomile and valerian root, may help ease anxiety.
- Acupuncture and Massage Therapy – Can support relaxation and stress management.
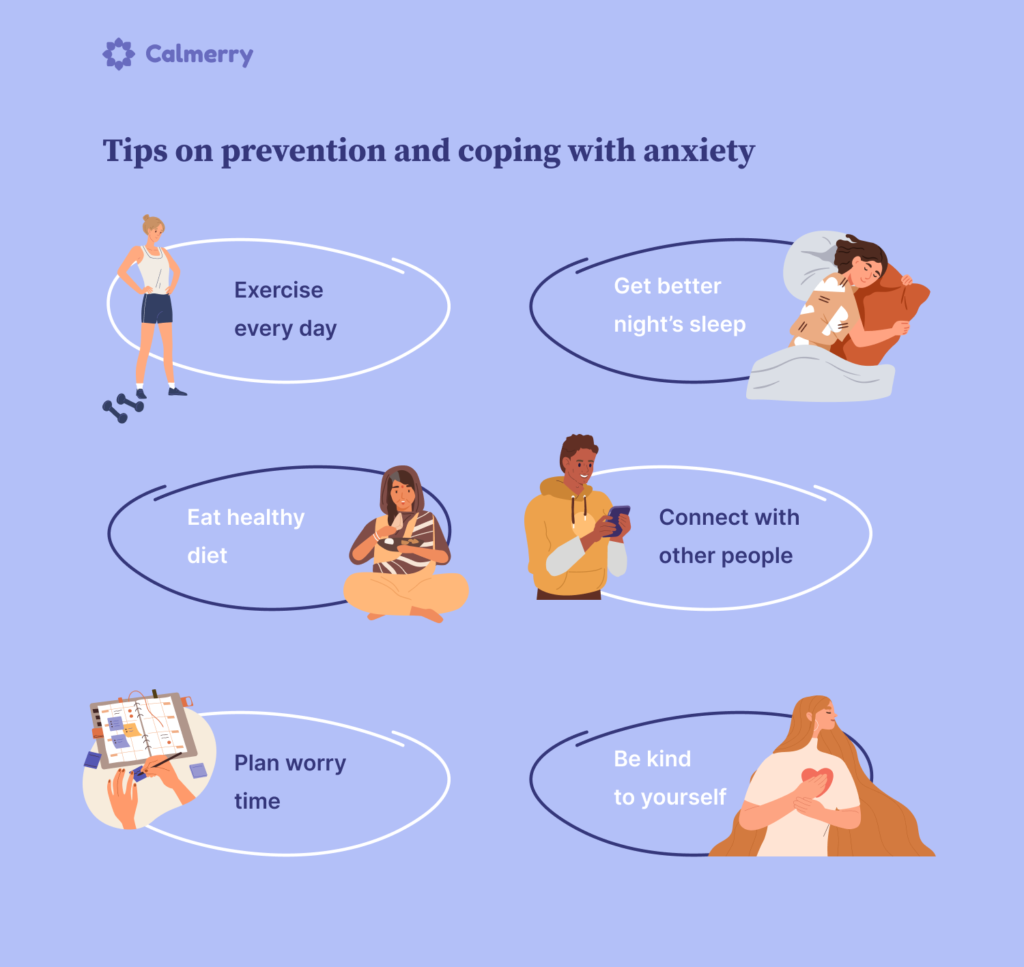
Coping Mechanisms and Lifestyle Changes
In addition to professional treatment, lifestyle changes can help manage anxiety:
1. Practice Deep Breathing and Relaxation Techniques
- Deep breathing exercises (e.g., diaphragmatic breathing) reduce physiological stress responses.
- Progressive muscle relaxation (PMR) helps relieve tension and calm the mind.
2. Regular Exercise
- Engaging in physical activity releases endorphins, reducing stress and improving mood.
- Activities like jogging, swimming, or yoga can be particularly beneficial.
3. Maintain a Healthy Diet
- Eating a balanced diet rich in whole foods, lean proteins, and healthy fats supports brain function.
- Limiting caffeine, sugar, and processed foods can prevent worsening anxiety symptoms.
4. Improve Sleep Hygiene
- Establishing a consistent sleep schedule helps regulate mood and stress levels.
- Avoiding screens before bedtime and creating a relaxing bedtime routine can promote better sleep.
5. Limit Alcohol and Caffeine Intake
- Reducing alcohol and caffeine consumption can help prevent anxiety spikes and improve overall well-being.
6. Engage in Social Support
- Talking to trusted friends, family, or support groups provides emotional relief and encouragement.
- Seeking professional help when needed ensures access to effective coping strategies.
7. Practice Time Management
- Organizing tasks and setting realistic goals prevent feeling overwhelmed.
- Breaking large tasks into smaller steps improves productivity and reduces stress.
Conclusion
Anxiety disorders can be overwhelming, but they are treatable with the right approach. Understanding different types, identifying causes, and implementing effective coping strategies can significantly improve mental well-being. If you or someone you know is struggling with anxiety, seeking professional help is the first step toward a healthier, more balanced life.