Acne is one of the most common skin conditions affecting millions of people worldwide, regardless of age. Although it is typically associated with teenagers, acne can persist into adulthood, and in some cases, it may even develop later in life. Acne can have a significant impact on both the physical appearance and mental well-being of individuals. It often leads to low self-esteem, emotional distress, and social anxiety. Fortunately, effective treatment methods and preventive measures are available. In this article, we will explore the causes, symptoms, treatment options, and tips to prevent acne to help you achieve healthier, clearer skin.
Table of Contents
- Introduction: What is Acne?
- Causes of Acne
- 2.1 Hormonal Imbalance
- 2.2 Excess Oil Production
- 2.3 Bacterial Growth
- 2.4 Clogged Pores
- 2.5 Genetics
- Symptoms of Acne
- Impact of Acne on Skin Health
- Effective Treatment Methods for Acne
- 5.1 Topical Treatments
- 5.2 Oral Medications
- 5.3 Light and Laser Therapy
- 5.4 Chemical Peels
- 5.5 Natural Remedies
- Prevention Tips for Acne
- Conclusion: Achieving Clearer Skin
Introduction: What is Acne?
Acne is a chronic skin condition that occurs when hair follicles are clogged with oil, dead skin cells, and sometimes bacteria. This leads to the formation of pimples, blackheads, whiteheads, cysts, and even abscesses. Acne primarily affects areas of the skin that have a high number of sebaceous (oil) glands, such as the face, chest, shoulders, and back.
Although acne is not typically a serious health condition, it can have a significant impact on one’s self-confidence and emotional well-being. Moreover, untreated acne can lead to scarring, which may result in permanent skin damage.
Causes of Acne
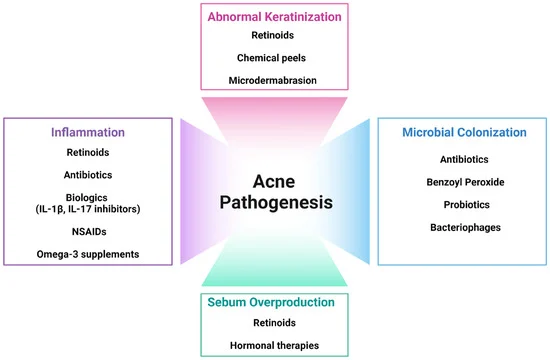
Acne occurs when the sebaceous glands produce excess oil (sebum) that mixes with dead skin cells, blocking the hair follicles and pores. Several factors contribute to acne formation, including hormonal changes, bacterial growth, and genetics.
2.1 Hormonal Imbalance
One of the most common triggers of acne is hormonal imbalance, particularly during puberty, menstruation, pregnancy, or the use of birth control pills. These hormonal fluctuations can increase oil production in the skin, leading to clogged pores and acne. Additionally, conditions like polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) can contribute to hormonal imbalances and acne.
2.2 Excess Oil Production
The sebaceous glands in the skin produce oil to keep the skin moisturized. However, when the body produces too much oil, it can mix with dead skin cells, clogging the pores and leading to acne. Excessive oil production can be caused by factors such as hormonal changes, diet, and medications.
2.3 Bacterial Growth
The bacteria Propionibacterium acnes is naturally found on the skin. However, when pores become clogged with oil and dead skin cells, it creates an environment for these bacteria to multiply. This bacterial overgrowth can lead to inflammation, resulting in pimples, cysts, or abscesses.
2.4 Clogged Pores
Clogged pores are a primary cause of acne. When oil, dead skin cells, and dirt block the pores, they create an ideal environment for bacteria to thrive. The result is the formation of pimples, blackheads, and cysts.
2.5 Genetics
Genetics play a significant role in acne development. If your parents had acne, you’re more likely to develop the condition yourself. Genetic factors may also influence how your skin reacts to environmental factors like stress, diet, and skin care products.
Symptoms of Acne
Acne symptoms can vary from mild to severe. The most common symptoms include:
- Pimples (Pustules): Raised red bumps with white or yellow centers filled with pus.
- Blackheads: Small, dark spots caused by clogged pores that are open to the air.
- Whiteheads: Similar to blackheads but with closed pores.
- Cysts and Nodules: Deep, painful, large bumps beneath the skin’s surface.
- Inflammation: Red, swollen, and tender skin surrounding the acne lesions.
Severe acne may cause scarring, which can be permanent and affect your skin’s appearance.
Impact of Acne on Skin Health
While acne itself may not pose serious health risks, it can lead to long-term skin issues. The primary concerns include:
- Scarring: Acne lesions can cause scars if not treated correctly, leaving permanent marks on the skin.
- Hyperpigmentation: Dark spots or patches may remain after acne heals, often referred to as post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation.
- Emotional and Psychological Effects: Persistent acne, especially when severe, can lead to anxiety, depression, and low self-esteem.
It’s important to address acne early to reduce the risk of these long-term effects.
Effective Treatment Methods for Acne
There are various treatment options available to help manage acne and prevent further breakouts. These range from topical treatments to more advanced procedures.
5.1 Topical Treatments
Topical treatments are often the first step in treating acne. These include over-the-counter (OTC) creams, gels, or lotions that contain ingredients such as:
- Benzoyl Peroxide: Helps to kill acne-causing bacteria and reduce inflammation.
- Salicylic Acid: Exfoliates the skin, removing dead skin cells and preventing clogged pores.
- Retinoids: Derived from Vitamin A, retinoids help unclog pores and promote skin cell turnover.
5.2 Oral Medications
For moderate to severe acne, oral medications may be prescribed by a dermatologist. These include:
- Antibiotics: To reduce inflammation and bacteria in the skin.
- Hormonal Therapy: Birth control pills or anti-androgen medications can help regulate hormones, particularly in women with acne linked to hormonal imbalances.
- Isotretinoin (Accutane): A potent oral medication used for severe, cystic acne that does not respond to other treatments.
5.3 Light and Laser Therapy
Light and laser therapies, such as blue light therapy or fractional laser treatments, are becoming increasingly popular for treating acne. These treatments target the bacteria responsible for acne and reduce oil production, helping to clear up breakouts.
5.4 Chemical Peels
A chemical peel involves applying a solution to the skin that exfoliates and removes the top layer of dead skin cells. This can help unclog pores, reduce acne, and improve skin texture and appearance.
5.5 Natural Remedies
Some people turn to natural remedies to help manage mild acne. These include tea tree oil, aloe vera, honey, and green tea extract, all of which have anti-inflammatory and antimicrobial properties that can help reduce acne symptoms.
Prevention Tips for Acne
Preventing acne requires consistent skincare, healthy lifestyle choices, and the right habits to keep your skin clear. Here are some tips to help prevent breakouts:
6.1 Maintain a Consistent Skincare Routine
A proper skincare routine involves cleansing, exfoliating, and moisturizing regularly. Use gentle products suitable for your skin type and avoid over-washing, as this can irritate the skin and exacerbate acne.
6.2 Avoid Touching Your Face
Touching your face frequently can transfer dirt, oil, and bacteria to your skin, contributing to acne. Try to keep your hands off your face as much as possible, especially when your hands are dirty.
6.3 Use Non-Comedogenic Products
Choose skincare and makeup products labeled as “non-comedogenic,” meaning they are formulated to avoid clogging pores. This helps prevent the formation of blackheads and whiteheads.
6.4 Stay Hydrated and Eat a Healthy Diet
Drinking plenty of water and eating a balanced diet can help keep your skin healthy. Avoid excessive consumption of sugary foods and dairy products, as these may trigger breakouts in some individuals.
6.5 Manage Stress Effectively
Stress can trigger hormonal fluctuations, leading to acne flare-ups. Practices such as yoga, meditation, or deep breathing can help reduce stress and improve your skin’s condition.
Conclusion: Achieving Clearer Skin
Acne is a common and frustrating skin condition that can affect people of all ages. While it can be challenging to manage, understanding the causes, symptoms, and available treatment options can help you regain control of your skin health. By adopting a consistent skincare routine, seeking effective treatments, and making lifestyle changes, you can significantly reduce the impact of acne on your skin and overall well-being.