Health insurance reforms play an essential role in resolving healthcare inequalities among poor communities. These medical policy reforms enhance both coverage range and affordability to provide equal access to top-quality healthcare services.
The article evaluates health insurance reform effects on underprivileged communities through an analysis of expanded coverage and lower out-of-pocket expenses along with enhanced healthcare benefits.
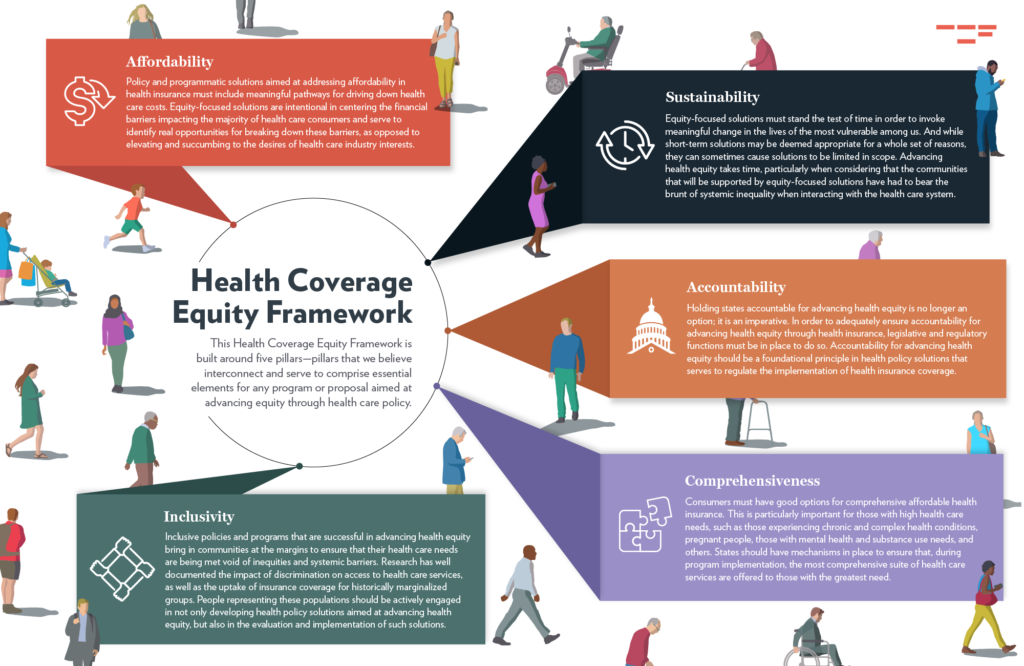
Introduction: The Need for Health Insurance Reforms
- Individuals who belong to low-income categories encounter substantial obstacles when attempting to obtain healthcare because their numbers consist of high percentages of people without insurance combined with minimal financial means.
- The Affordable Care Act (ACA) combined with other health insurance reforms in the United States functions to increase coverage and decrease costs specifically for the low-income population.
- Healthcare reforms exist to expand medical care availability together with reducing costs while enhancing quality healthcare services for communities without proper medical care. Health insurance reforms executed in healthcare settings have significantly changed the medical service accessibility along with health results for people with low earnings.
- Lower income groups throughout history encountered major obstacles when trying to get necessary healthcare because both their insurance coverage rate was high and they had limited monetary resources. The Affordable Care Act (ACA) alongside other health insurance reforms functions as an important instrument that broadens healthcare coverage and decreases medical expenses specifically for those with low incomes.
- The proposed reforms endeavor to offer better care and reduced expenses and broader healthcare availability for people without adequate healthcare services. A fundamental part of the ACA involved Medicaid expansion because it enabled many additional low-income adults to receive healthcare benefits.
- Research studies prove Medicaid expansion reduces high medical costs and increases the personal income of low-income citizens. The reforms applied to health insurance analytics succeeded in reducing the number of uninsured people within low-income communities. A body of evidence demonstrates how the ACA lowered uninsurance rates both among those living in poverty and the residents of states that expanded Medicaid.
- Newly gained insurance coverage allows poorer members of society to obtain increased access to both preventive medicine and outpatient medical services. The expanded access to healthcare services because of these reforms leads to better health results while cutting down the need for emergency medical assistance.
- The acquisition of health care coverage improves both medical affordability and financial stability for low-income groups throughout the nation. Analysts discovered that medical bill difficulties together with medical debts decreased in population groups from expansion states when compared to states without expansion.
- Healthcare reforms through insurance systems have significantly diminished disparities because these changes expanded healthcare access for members of low-income groups. The expanded healthcare access resulted in enhanced health results that also decreased health disparities.
- Some low-income groups lack health insurance coverage mainly because their states never implemented Medicaid expansion. The availability of comprehensive healthcare depends on fixing all gaps in coverage for every member of the low-income demographic.
- The implementation of health insurance reforms delivered better access and more affordability to healthcare but such changes produce financial strains by elevating government healthcare costs. The policies that maintain financial stability together with universal access to healthcare require continued examination as a significant policy matter.
- Health insurance reforms have delivered substantial changes to populations with low-income through expanded healthcare coverage and better services accessibility and decreased disparities. The development of new measures to strengthen healthcare reforms must continue because it is essential for achieving health equity and universal quality medical care for all people despite their incomes.
Expansion of Coverage

🔘 Reduction in Uninsured
Rates Free healthcare insurance changes have produced major reductions in the number of people without health insurance among low-income populations. Research demonstrates that the ACA enacted major reductions in uninsurance coverage which affected the poor as well as residents of Medicaid expansion states. PMC.NCBI.NLM.NIH.GOV
🔘 Medicaid Expansion
The ACA implemented Medicaid expansion as its main component for achieving broader healthcare coverage. The evidence demonstrates that Medicare expansion cut down on unaffordable healthcare costs while leading to higher earnings for low-income beneficiaries.
KFF.ORG Improved Access to Healthcare Services Increased Utilization of Preventive and Outpatient Services The expansion of health insurance coverage allows low-income people to use preventive and outpatient medical services.
Greater healthcare access due to Medicaid expansion provides better health results and helps individuals avoid emergency situations. PMC.NCBI.NLM.NIH.GOV
🔘 Enhanced Financial Security
Health care coverage helps low-income groups achieve better financial security while making healthcare more affordable to them. Research presents evidence of decreased medical bill payment issues alongside reduced medical debt occurring more often in states which adopted expansion measures when compared to those states lacking the expansion.
KFF.ORG Reduction in Health Disparities Addressing Health Inequities Health insurance reforms successfully cut down health disparities because they offer essential healthcare services to people who lack sufficient income.
The expanded healthcare access has produced better health results while simultaneously minimizing health inequalities among people. PMC.NCBI.NLM.NIH.GOV
Challenges and Considerations
🔘 Coverage Gaps
The uninsured status of low-income people primarily affects non-Expanding-Medicaid states despite the overall advancement in coverage expansion efforts.
The achievement of complete healthcare coverage requires solving present insurance coverage deficiencies for low-income communities.
🔘 Financial Implications
The health insurance reforms brought improved health coverage yet they create financial difficulties which lead to greater government expenditure.
The financial aspect requires careful consideration along with the goal of providing equal healthcare access to solve this policy dilemma.
Conclusion
Health insurance reforms have positively affected low-income populations through increased coverage together with enhanced healthcare access and diminished health disparity.
The success of health insurance reforms depends on continuous improvement work to create more equity in healthcare services while establishing quality care availability for all people regardless of their income levels.