Introduction
Antimicrobial resistance (AMR) stands as a top immediate health threat that affects the global community. The World Health Organization (WHO) and international bodies caution about bacteria, viruses, fungi and parasites showing growing resistance to medical treatment drugs.
Research about antimicrobial resistance shows that the global need for joint resistance-curbing initiatives continues to increase.
This paper examines existing healthcare policies together with remedies that different countries have implemented to fight against Antimicrobial Resistance at the global level.
Understanding Antimicrobial Resistance (AMR)
- The phenomenon of antimicrobial resistance happens as microorganisms including bacteria and viruses and parasites alongside fungi develop resistance to medications that should eliminate or slow their development.
- Antibiotic agents lose their medical effectiveness to treat bacterial infections because bacteria have become more resistant to them.
- Medical professionals alongside livestock farmers and other users of antibiotics are responsible for AMR because of their repeated use of medications.
- Active bacterial strains disseminate quickly while generating challenging and expensive treatment conditions that lengthen hospitalization periods and increase financial expenses which produce elevated mortality rates.
- AMR requires worldwide initiatives to control this problem since it transcends national boundaries. Resistant pathogens travel effortlessly between nations by means of human travel and worldwide trade of food and animals.
- Medical professionals need to understand and handle the factors that contribute to AMR development for maintaining antimicrobial treatments’ power.
Global Impact of AMR on Health
AMR produces major health consequences that span throughout the entire world. Resistant bacteria infections share two major issues: they require more expensive and harder treatment methods which consequently lead to elevated mortality rates.
The main results connected to antimicrobial resistance consist of: Impact Details The death rates from resistant infections increase because standard treatments fail to work.
Patients who develop antibiotic-resistant infections need to stay in intensive care units longer which leads to their treatment duration extending beyond the normal period.
Medical institutions bear elevated antibiotic treatment expenses from employing advanced treatment methods together with non-traditional antibiotic medicines.
Medical procedures require effective antibiotics because their success depends on them. The lack of worldwide coordinated efforts will cause AMR to expand while harming worldwide economic stability along with healthcare structures and individual health conditions.
International governments and global organizations now create and execute new policies and corrective actions against antibiotic resistance at the worldwide scale.
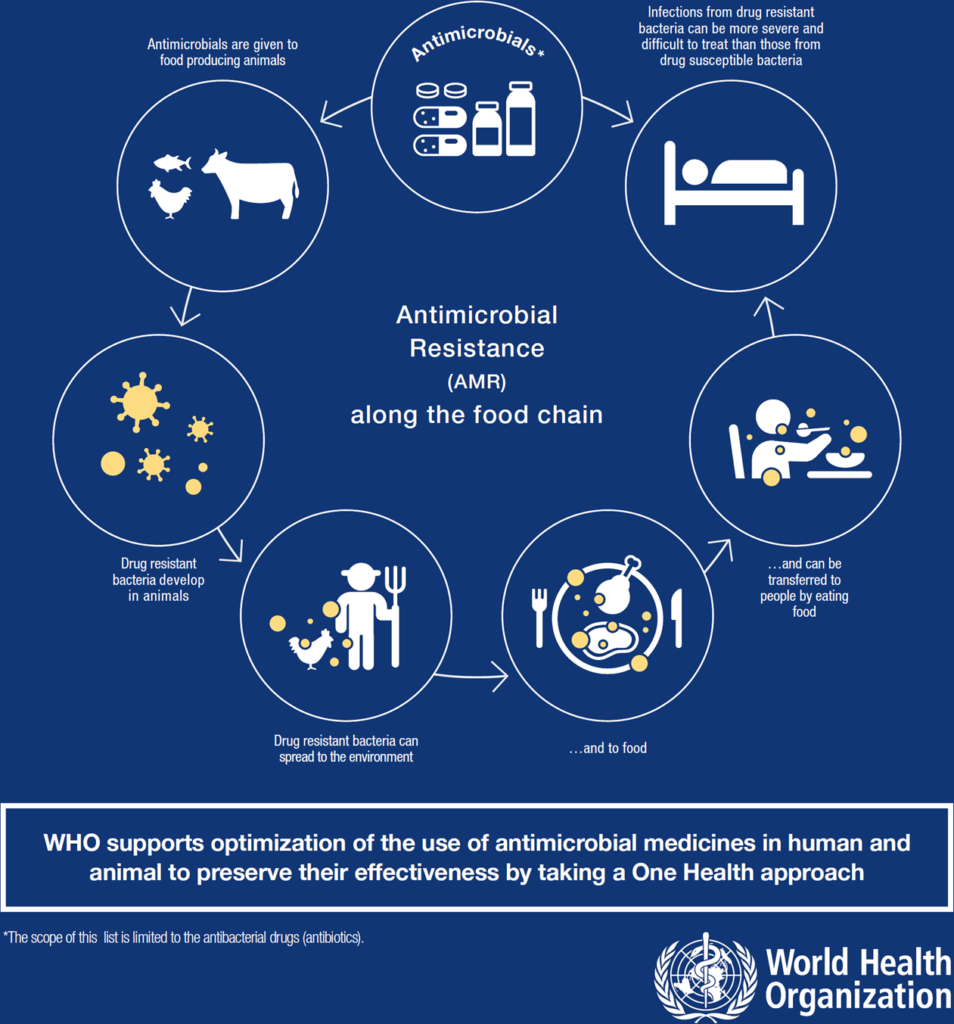
Recent Healthcare Policies to Combat AMR
Various new healthcare policies at global and national levels have been established to combat the growing menace of AMR. The purposes of new policies include limiting antibiotic abuses while implementing better infection control measures and creating new antimicrobial agents.
🔘 The World Health Organization (WHO) Global Action Plan
The WHO started the Global Action Plan on AMR in 2015 by presenting five major directives for implementation. Objective Details The world needs improved education regarding germs and antibiotics which targets both patients and medical staff.
Healthcare professionals must enhance infection prevention strategies so infections decrease in both healthcare facilities and public community environments.
The improvement of antibiotic usage involves the support of antibiotic stewardship methods to achieve optimal drug administration practices. An initiative exists to encourage the creation of new antimicrobial drugs as well as substitute treatment approaches.
The implementation of improved Antibiotic surveillance system requires better monitoring of antibiotic usage along with resistance patterns worldwide. Governments should create national AMR action plans as part of their collaborative effort to control resistance by exchanging research, resources and proven practices.
The WHO supports the integration of AMR into worldwide health plans and calls for partnership between health care systems alongside agricultural and environmental sectors.
| Objective | Details |
|---|---|
| Improving awareness | Educating the public and healthcare professionals about the dangers of AMR. |
| Reducing infection | Enhancing infection prevention and control in healthcare settings and communities. |
| Optimizing antibiotic use | Promoting antibiotic stewardship to ensure that antibiotics are used appropriately and effectively. |
| Developing new antibiotics | Stimulating the development of new antimicrobial agents and alternatives. |
| Strengthening surveillance | Improving global surveillance of antibiotic use and resistance patterns. |
🔘 National and Regional Initiatives
Different nations have implemented multiple policies for combating AMR. For example: Through the CARB National Action Plan the United States seeks to reduce antibiotic-resistant bacteria development by enhancing antibiotic use oversight and research and by conducting better surveillance.
The European Union introduced the One Health Action Plan on Antimicrobial Resistance to combine human health along with animals and environmental sectors in AMR control programs.
The Indian government created a National Action Plan on AMR which provides instructions about antibiotic stewardship along with surveillance enhancements.
Each area follows the WHO’s global tactics yet their execution differs depending on operational health systems and fiscal availability as well as administrative control structure.
🔘 Regulatory Policies in Agriculture and Healthcare
Organizations worldwide have established stricter regulations about antibiotic usage in animals since the agricultural use of antibiotics drives AMR development.
European Union member states enforced a total ban against using antibiotics as growth promoters in farm animals together with implementing specific medicinal antibiotic protocols for animal veterinary treatment.
The United States government created new policies to minimize food animal intake of antibiotics which now focus on medicinal purposes instead of growth promotion benefits.
Healthcare establishments have adapted regulations to establish appropriate use of antibiotics. Antibiotic stewardship programs have become mandatory in various hospitals because they make healthcare providers evaluate antibiotic needs and select proper medication dosage duration.
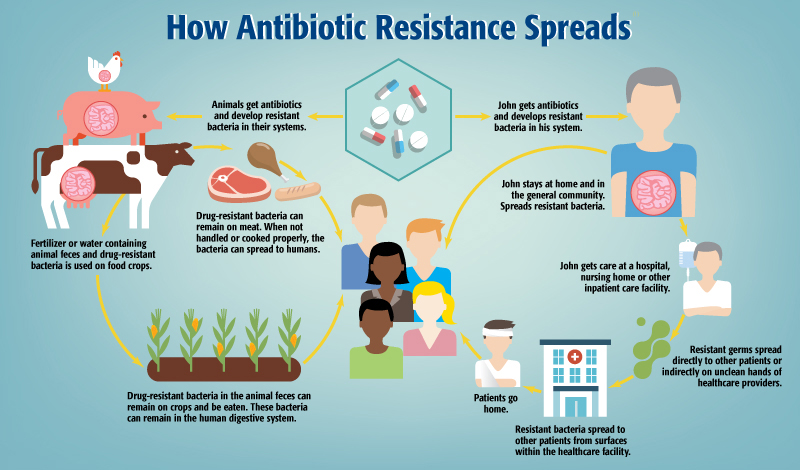
Remedies to Combat AMR
The fight against Antibiotic-Resistant Infections needs both essential healthcare policies along with practical remedies for effectiveness. Various global remedies along with major strategies have emerged for fighting AMR.
🔘 Antibiotic Stewardship Programs
ASPs represent essential tools which healthcare facilities use to combat antimicrobial resistance. Such programs work to achieve proper antibiotic utilization thus minimizing resistant bacteria.
The goals of ASPs include: Strategy Details Antibiotic prescription needs optimization to restrict their use to appropriate medical situations. Healthcare institutions should monitor antibiotic treatment to detect patterns where healthcare providers utilize antibiotics excessively or incorrectly.
| Strategy | Details |
|---|---|
| Optimizing antibiotic prescribing | Ensuring that antibiotics are prescribed only when necessary and appropriate. |
| Monitoring use | Tracking antibiotic use to identify patterns of overuse or misuse. |
| Education and training | Educating healthcare providers about the responsible use of antibiotics. |
Teachers of healthcare providers should receive training about proper antibiotic utilization. Academic detailing projects from ASPs continue to spread throughout healthcare facilities worldwide where medical professionals have proven their capability to decrease antibiotic misuse.
🔘 Improved Diagnostics and Surveillance
Diagnosis success is vital for fighting antimicrobial resistance. The quick diagnostic tests enable doctors to recognize infection sources so they can select appropriate antibiotics for treatment.
Essential for making informed policy decisions in healthcare together with selection of appropriate treatments is the worldwide collection of antibiotic resistance data.
Technology Impact Ambulatory healthcare professionals can use rapid diagnostic tests which provide faster detection of pathogen resistance.
The worldwide surveillance of antibiotic resistances enables medical authorities to develop better treatment guidelines. Faster and more precise diagnostic methods help healthcare providers avoid administering broad spectrums of antibiotics which decreases the development of drug-resistant organisms.
🔘 Development of New Antibiotics and Alternatives
The solution to AMR demands both new antibiotic medications and additional choices beyond conventional antimicrobial therapeutic options.
Pharmaceutical organizations and governmental establishments together with scientific research institutions dedicate funding to create new antibiotics against pathogens that show drug resistance.
The medical field explores phage therapy and antimicrobial peptides as alternative antimicrobial compounds to traditional antibiotics.
Approach Details Researchologists work on developing fresh antibiotic categories which treat infections that resist current treatments.
Bacteriophages also known as viruses that kill bacteria function as an alternative treatment option. The essential matter for replenishing antibiotic reserves requires governments to focus on stimulating investment programs dedicated to antibiotic research and development.
🔘 Public Education Campaigns
The battle against AMR requires public awareness efforts which educate people about proper antibiotic treatment while curbing the need for unneeded prescriptions. World governmental bodies together with the WHO currently run international education programs which teach:
The risks of unsanctioned antibiotic usage mandate patients to stay away from consuming antibiotics beyond medical supervision. Implementation of prescribed antibiotics requires patients to complete their full treatment as neglecting this step leads to antibiotic resistance development.
These public awareness activities operate to combat antibiotic misuse while developing better antibiotic usage ethics.
Challenges in Implementing Global AMR Policies
Several obstacles remain in the process of implementing universal AMR policies throughout the world. Challenge Details Most low-income countries find it difficult to allocate resources toward AMR efforts while building sufficient healthcare facilities.
Some regions experience poor political dedication toward making AMR a focus point in their health strategies. The international scope of AMR demands border-crossing collaboration but this proves demanding because national policies and interests differ from one another.
Effective combat against antimicrobial resistance demands continuous international cooperation together with sufficient funding to prevent wildlife deaths from multiplication.
Conclusion
Urgent action needs to be taken because antimicrobial resistance threatens people globally. The world can control antimicrobial resistance by adopting new healthcare regulations and developing diagnostic systems and antibiotic stewardship methods along with antibiotic treatments.
Extreme action towards controlling AMR depends on worldwide partnerships together with government support and sufficient financial backing.
Taking essential measures to address AMR origins while enhancing monitoring systems together with good antibiotic practice will ensure future populations remain protected from antimicrobial resistance’s destructive outcomes.